Manufacturing activities
Energy Saving in Global Production
Most CO2 emissions in the manufacturing process come from the consumption of energy generated by fossil fuels. Nissan engages in a variety of energy-saving activities in the manufacturing process in pursuit of the lowest energy consumption and CO2 emissions of any automobile manufacturer.
In the realm of automotive production technology, we are introducing highly efficient equipment and improving manufacturing techniques. Other key approaches are the three-wet paint process and low-temperature baking technology used for vehicle painting, which enables the body and bumpers to be painted at the same time. Approximately 30% of CO2 emitted from manufacturing plants comes from the painting process, thus shortening or eliminating processes and lowering temperatures during the process will lead to a reduction in CO2 emissions. The low-temperature three-wet painting technology introduced by Nissan enables the body and bumpers, which were previously painted separately, to be painted at the same time, reducing CO2 emissions from the painting process by 25% or more. Nissan has implemented this technology in the new production line at the Tochigi Plant (launched in 2021) and will gradually expand its roll out as painting facilities become more sophisticated in the future. Also, systems for recycling air expelled from booths for reuse needed dehumidifying processing to ensure that the air was at the humidity required. Dry paint booths can reuse air without dehumidifying it, reducing energy consumption to less than half its previous levels. This technology was adopted for the dry paint booths at our Sunderland Plant in the U.K. (operating since September 2018) and has also been implemented on the new line at the Tochigi Plant.
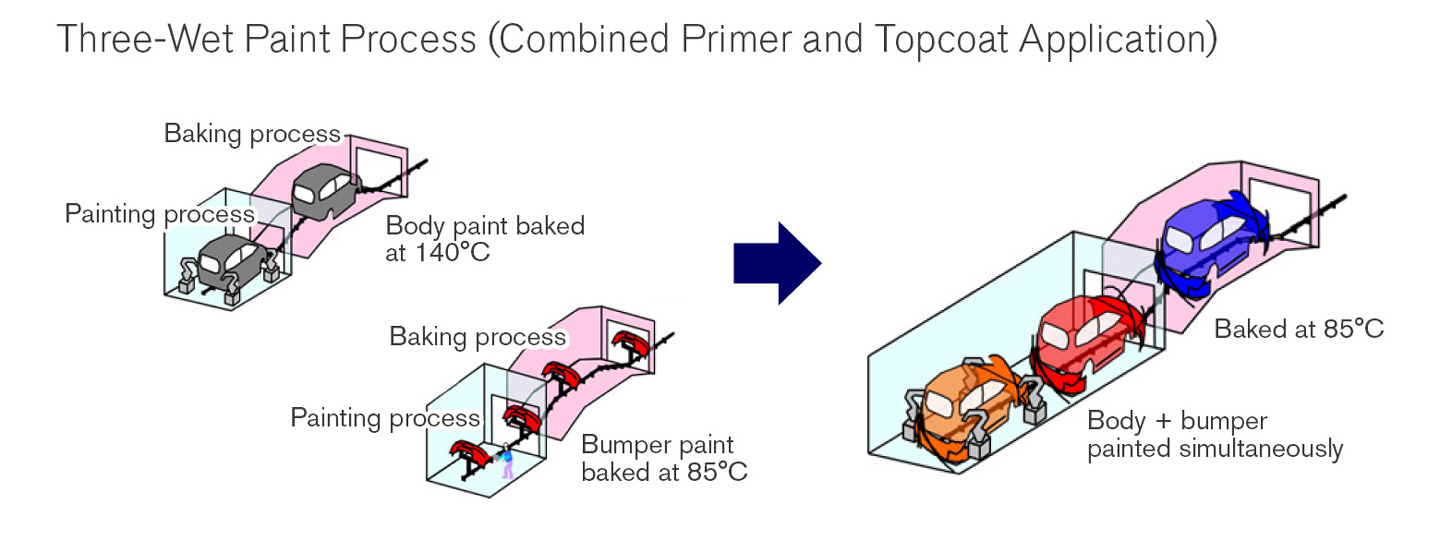
Simultaneous Painting of Body and Bumpers
CO2 emissions have been reduced by simultaneously painting the body and bumpers using a new technology and consolidating them into one process (right) and drying at a low temperature (85oC) instead of the conventional two-step process (left).
To reach the defined objectives for CO2 emissions and the use of energy, Nissan solicits proposals from each global site, preferentially allocating investment based on the benefit in CO2 reduction compared to project costs. By making value of carbon one key factor in internal evaluations, Nissan enables more efficient investment and greater competitiveness.
Nissan plants use finely controlled lighting and air conditioning for low-energy-use and low-energy-loss operations. The company is promoting CO2 emission reduction activities and introducing cutting-edge energy-conservation technology from Japan to its plants worldwide. Meanwhile, Nissan plants in all countries learn and share best practices with each other.
In addition, Nissan Energy Saving Collaboration (NESCO) diagnoses energy loss at the plants and proposes new energy-saving countermeasures. A NESCO team was established for Japan in 2003, and teams for Europe, Mexico and China in 2013. A NESCO team has also been launched to support energy-saving efforts at Alliance partner Renault. Nissan takes into consideration the balance of CO2 emissions for the entire company, its renewable energy usage rate and cost when sourcing the energy it uses. Choosing the best suited suppliers for achieving CO2 reduction targets is a key activity for Nissan.

