Carbon neutrality
Toward the Realization of Carbon Neutrality in 2050
To achieve carbon neutrality across the Company’s operations and product life cycle by 2050, Nissan’s aim is for every all-new Nissan vehicle offering in key markets to be electrified by the early 2030s, and to this end, will promote innovations in electrification and manufacturing technologies in the following strategic areas:
- Battery innovations for cost-competitive and more efficient EVs
- Greater energy efficiency of our e-POWER electrified powertrains
- Develop of a battery ecosystem to support decentralized renewable energy generation
- Greater energy and material efficiencies during the manufacturing process
Our response to climate change
Response to climate change is one critical issue that must be addressed globally, thus international long-term goals have been discussed since the adoption of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in 1992. At the Climate Change Summit in April 2021, the leaders of 40 countries and regions gathered with the aim of realizing carbon neutrality in 2050 and announced CO2 emission targets leading up to 2030.
To contribute to the resolution of global climate change issues, Nissan formulated a long-term vision based on the 2°C scenario in the 2006 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report, achieving sustainable success through the steady achievement of retroactive milestones. In 2020, we conducted a scenario analysis* regarding the opportunities and risks posed by climate change and exanined in term of business resilience based on assumptions about society taken from the International Energy Agency (IEA) 4°C and 2°C scenarios, as well as the IPCCs 1.5°C Special Report.
To avoid risks such as these to the extent possible and create future opportunities, Nissan is leveraging knowledge gained from scenario analysis for use in actual activities and reviewing strategies for expanding resilience. We believe it is important to more clearly and accurately communicate these impacts and the strategies considered to investors and other stakeholders. Nissan supports the TCFD's recommendations and will strive to disclose information in line with its recommended framework. (TCFD: The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures)
In fiscal 2021, we have started a financial impact assessment, based on the scenario analysis that we have already disclosed. Below are the results of our assessment of the impact of carbon taxes.
Background of Financial Impact Assessment Scenario Selection
Pricing for CO₂ emissions is progressing, and an increasing number of countries and regions are introducing carbon taxes. Although the level of taxation and the industries subject to the tax vary by country and region, this analysis will focus on the financial impact of the carbon taxes due to its significant impact on companies.
Evaluation of calculation methods and estimated taxes, assumptions
In our calculations, we referred to the IEA report and other reports on carbon taxes as the basis for our carbon tax projection.
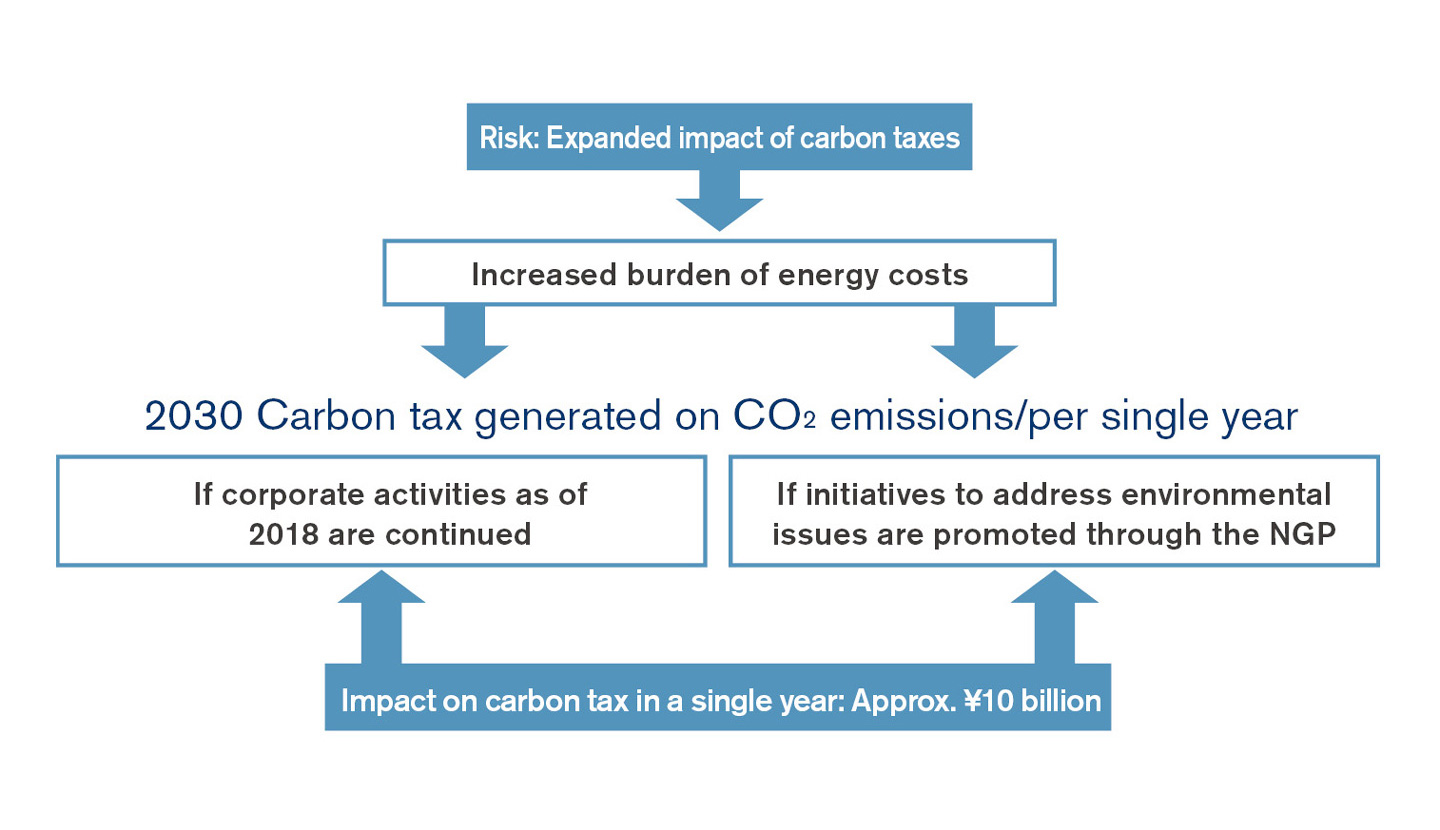
The carbon tax on GHG emissions in 2030 was calculated by comparing cases where:
1) Corporate activities as of 2018 have been continued, and
2) The Nissan Green Program promotes environmental activities and the impact of annual carbon tax could be curbed
Impact on Business Outlook
We estimated that the carbon tax impact of Scope 1 & 2 could be kept to approximately ¥10 billion if the environmental issues addressed in the Nissan Green Program were implemented, compared to the case where GHG emissions were not reduced.
Further, in January 2021, we announced a new goal for achieving carbon neutrality in 2050, throughout the vehicle lifecycle, such as material extraction, manufacturing, vehicle use and vehicle recycling or reuse at end-of-life. Nissan considers CO2 emissions not only when the vehicle is running, but throughout the value chain, including suppliers, from the procurement of raw materials to transportation. We are developing new technologies and strive to reduce CO2, including strengthening the use of renewable energy in the manufacturing process.
Battery innovations for cost-competitive and more efficient EVs
Battery Technology Innovations
We are developing batteries according to a long-term roadmap. We are seeking economies of scale and greater competitiveness in technology by aligning specifications and increasing commonization within the Alliance. Moreover, Nissan continues working on battery innovations including development of battery materials that reduce the amount of cobalt used and all-solid-state batteries. At the same time, with regard to battery costs, we plan to achieve a profitability equivalent to that of internal combustion engines by 2030, working with suppliers to pursue further optimization of battery pack designs and manufacturing process rationalization.
Safety is Essential for the Adoption of Electric Vehicles
Safety is one of Nissan's most important requirements in developing and providing electric vehicles. We increase battery energy density to improve performance while conducting tests under various harsh conditions to ensure safety and reliability before releasing batteries in the market. The Nissan LEAF has sold 580,000 units (as of March 31, 2022) since the launch of first-generation model production, evidence that no serious accidents caused by batteries have occurred. Going forward, Nissan will ascertain the various environments in which our customers use their vehicles from market driving data, incorporate this data into advanced reliability design and experimental standards, reflect it in development, and contribute to the spread of EVs and the realization of mobility free from CO2 emissions.
Greater energy efficiency of our e-POWER electrified powertrains
Development of e-POWER
e-POWER is Nissan’s proprietary powertrain, using a gasoline engine to generate electricity for the electric motor that propels the vehicle. e-POWER achieves top-level fuel efficiency as well as nimble responsiveness, smooth acceleration and remarkable quietness while driving.
Based on the idea of creating a totally new type of electric vehicle, e-POWER first debuted in Japan on the Note compact car in November 2016. In March 2018 an e-POWER version of the Serena minivan was launched, which was followed by the all-new Kicks SUV e-POWER in June 2020. In December of the same year the all-new Note was launched exclusively with the evolved, second-generation e-POWER system. These models were well received, and as of March 31, 2021, cumulative domestic sales of e-POWER exceeded 500,000 units.
With the aim of achieving carbon neutrality, by the early 2030s, every all-new Nissan vehicle offering in Japan and all key markets will be electrified. To this end, we are promoting research and development that will substantially contribute to the elimination of carbon. Nissan announced breakthrough in engine efficiency, reaching 50% thermal efficiency with its in-development, next generation e-POWER system.
Nissan’s latest approach to engine development has raised the bar to world-leading levels, accelerating past the current auto industry average range of 40% thermal efficiency, making it possible to even further reduce vehicle CO2 emissions.
Nissan continues to accelerate innovation of these electrification technologies as one of the major pillars until battery EV spread everywhere.

Develop of a battery ecosystem to support decentralized renewable energy generation
Creating Value though the Reuse of Batteries
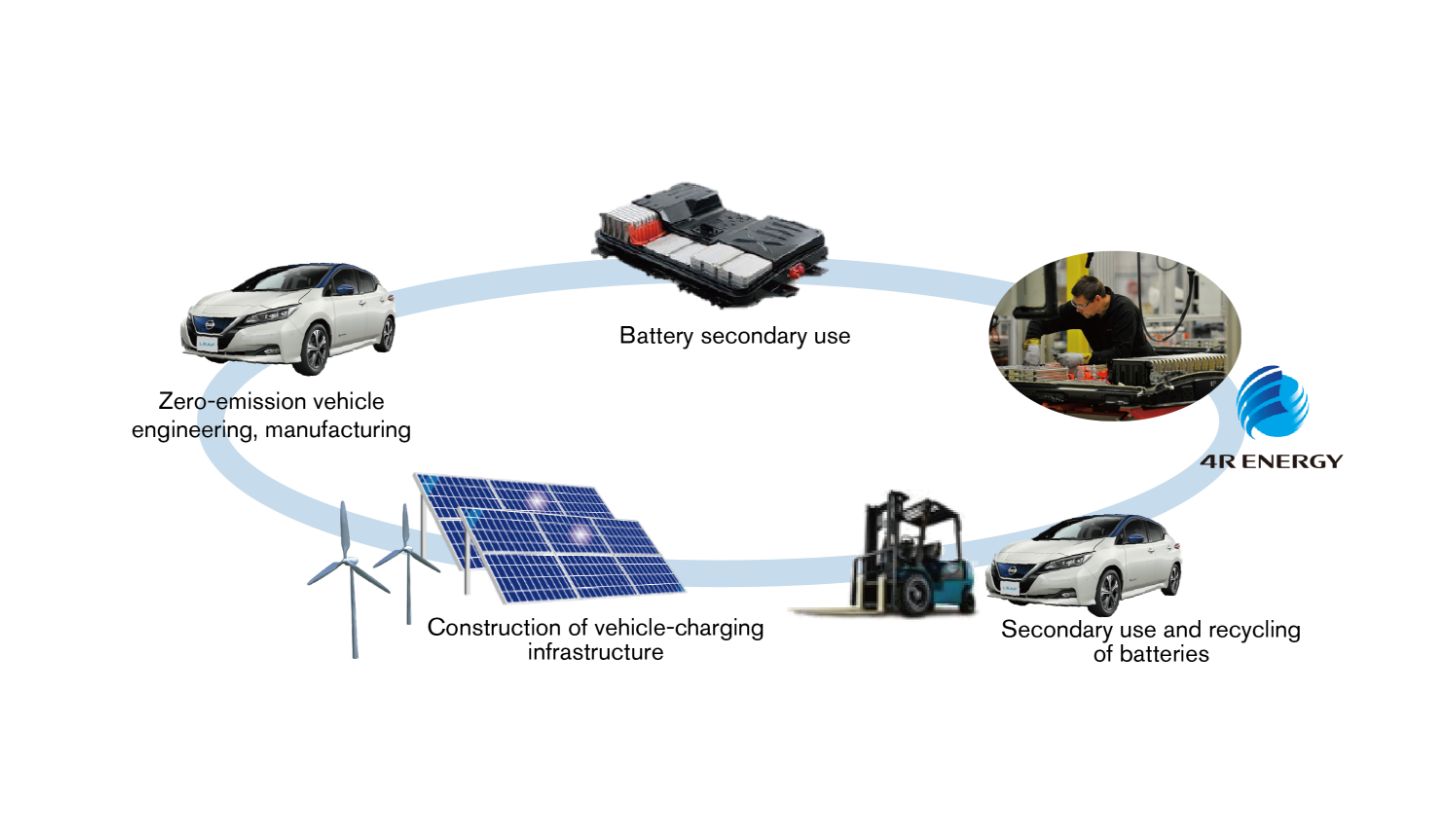
Nissan and Sumitomo Corporation established a joint-venture company 4R Energy Corporation in September 2010 to conduct research on the secondary usage of lithium-ion batteries that have been used previously in electric cars.
Naming a second-life business for recyclable advanced lithium-ion batteries as the "4R Energy" business in October 2009, both companies started a joint study to "Reuse, Resell, Refabricate and Recycle" the lithium-ion batteries used in electric cars. In March 2018, 4R Energy Corporation inaugurated the Japan’s first plant specializing in the reuse and recycling of lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles, in the town of Namie in Fukushima Prefecture.
By expanding this model into a business, we will realize increased EV value through the reuse of batteries, contributions to reducing resource dependency on the precious metals required for batteries and reduced CO2 during battery production so that we will drive the increased spread of electric vehicles. Additionally, we will contribute to the expansion of renewable energy by providing renewable batteries that are safe, reliable and highly price competitive.
Toward the Realization of a Future Mobility Society
Cutting-edge automotive technologies centered on EVs benefit customers who own cars as products, as well as contribute to the enrichment of everyone’s daily lives throughout society. Nissan is also engaged in research on systems that adjust power supply and demand connecting energy storage to the power grid using reused batteries. We offer Nissan Energy*1, a solution further enhancing the attractiveness of EVs by utilizing the storage and discharge functions of batteries installed in EVs. One of these, Nissan Energy Share, incorporates V2X technologies (V2L, V2H, V2B, V2G) using (sharing) electric power stored in the EV for a variety of applications, enabling the supply of electricity to homes and society as mobile storage batteries. In 2012, we launched the “LEAF to Home” system supplying electricity stored in Nissan LEAF batteries to homes and we are also conducting research into systems that adjust power supply and demand by connecting energy storage using recycled batteries to the power grid. We will make full use of advanced safety, autonomous driving, electrification and connected technologies accumulated up to now. Also, in cooperation with local governments, we aim to create an environment in which everyone can move with peace of mind, and at the same time, we are verifying the new business models created as a result of these efforts.
Blue Switch Program
In Japan, Nissan is engaged in the “Electrify Japan: Blue Switch” program. In conjunction with local governments and companies, the program promotes the use of EVs to address local issues related to the environment, disaster prevention, energy management, population declines, assistance for people with less access to transportation and tourism. At the same time, we aim to realize a resilient society that excites the people who lives there.
The high-capacity lithium-ion battery installed in the Nissan LEAF contributes to powerful driving performance and provides value as a mobile power source. In recognition of this value, Nissan has concluded agreements with many local governments and companies across Japan that utilize the Nissan LEAF as an emergency power source in the event of power outages caused by disasters or other unforeseen events.
Examples of fully leveraging the advantages of electric vehicles include using the Nissan LEAF to reduce energy costs and CO2 emissions, field operation test of energy management by virtual power plants*2, and car sharing services as eco friendly transportation options in sightseeing areas.
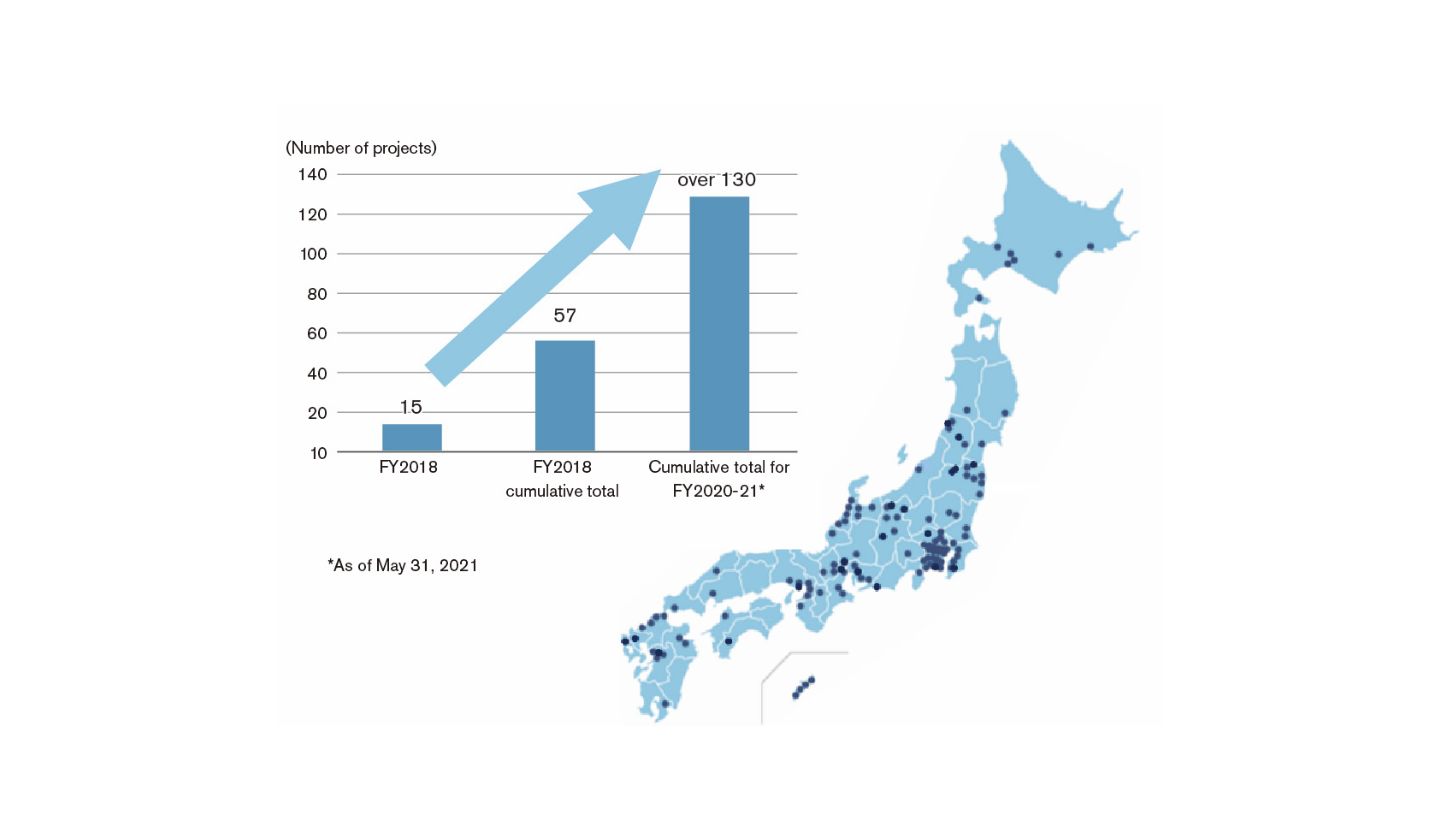
Since its launch in 2018, Nissan has signed over 172 agreements under the Blue Switch programs.
- Virtual power plant is a system that integrates several types of power sources, for examples, power generation, energy storage batteries and electric vehicles owned by local government, companies and residential customers, using information technologies such as IoT to function as they were a single power plant.
Experiments Using Nissan LEAF V2G Technologies in Germany
Nissan is engaged in global initiatives utilizing EV batteries. In December 2019, Nissan launched the "i-rEzEPT*" project together with Bosch.IO and the Fraunhofer Institutes IAO and IFAM. The project is also supported by the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure. This project aims to verify the effective use of renewable energy by combining Nissan LEAF charging with the power generated by residential solar panels and power supplied from the Nissan LEAF to homes and the power grid. At the same time, we will verify the effects of reducing public power grid loads and lowering the overall cost of owning EVs. Nissan is leading the project by providing the Nissan LEAF and chargers to 13 households with solar power systems. This project will end in October 2021, with the report publication scheduled for 2022.
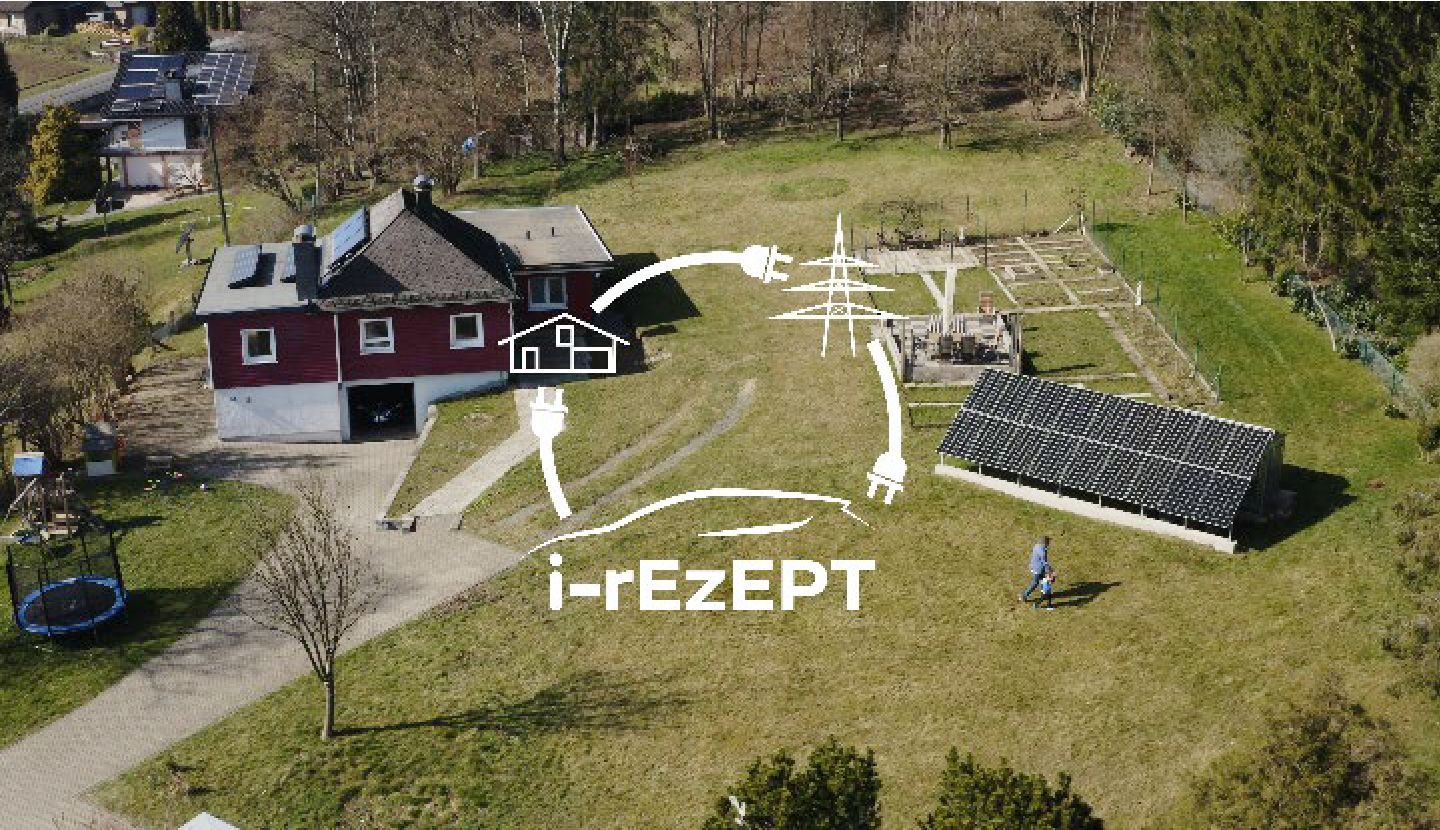

- i-rEzEPT stands for intelligente rückspeisefähige Elektrofahrzeuge zur Eigenstrommaximierung und Primärregelleistungsmarkt-Teilnahme, which in English means “intelligent regenerative electric vehicles for self-power maximization and primary control market participation.”
Building Communities with a Sustainable Future
To realize carbon neutrality and provide mobility services with a sustainable future, Nissan is making efforts to utilize Nissan innovations for the enrichment of people in the local community.
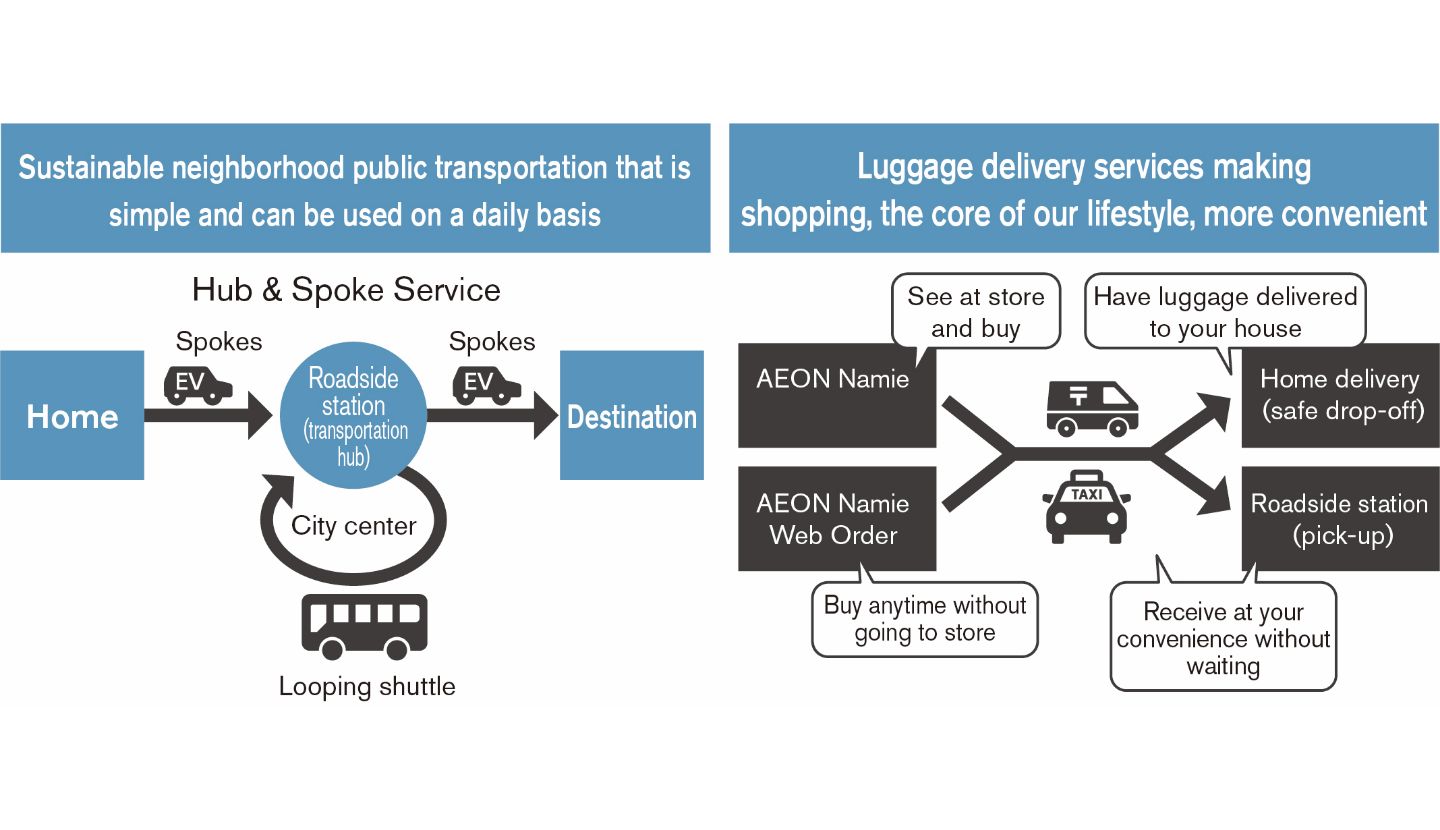
In early February 2021, Nissan, the three municipalities of Namie, Futaba and Minamisoma in Fukushima Prefecture, and eight companies including 4R Energy and local dealerships concluded the agreement to develop new modes of the transportation, and to promote the use of renewable energy in the Hamadori area of Fukushima. In recovering, from the Great East Japan Earthquake the overall goal is to help develop a revitalized, resilient and sustainable low-carbon community.
In addition, as a member of Namie Smart Mobility Challenge Secretariat organization, Nissan conducted a field operation tests of new mobility services in February 2021.This tests aimed to resolve issues of public transportation at Namie. Using only electric vehicles, it included running an autonomous vehicle on a route around central Namie to operate EV shuttle service.The long-term vision is to create sustainable transportation services that offer convenience in depopulated area.
Greater energy and material efficiencies during the manufacturing process
Nissan Intelligent Factory
Along with efforts to realize carbon neutrality through products and energy management, Nissan Intelligent Factory, the new production methods, will be introduced to build electrified, intelligent and connected cars. Nissan Intelligent Factory will contribute to further CO2 reductions through making production operations more flexible, efficient and sustainable.
For example, Nissan has developed a water-based paint that maintains the right viscosity at low temperatures, so that bodies and bumpers can be painted together. This will cut carbon dioxide emissions from the process by 25%. Nissan will also use a water-free painting booth that makes it possible to collect all waste paint and reuse it in other production processes.
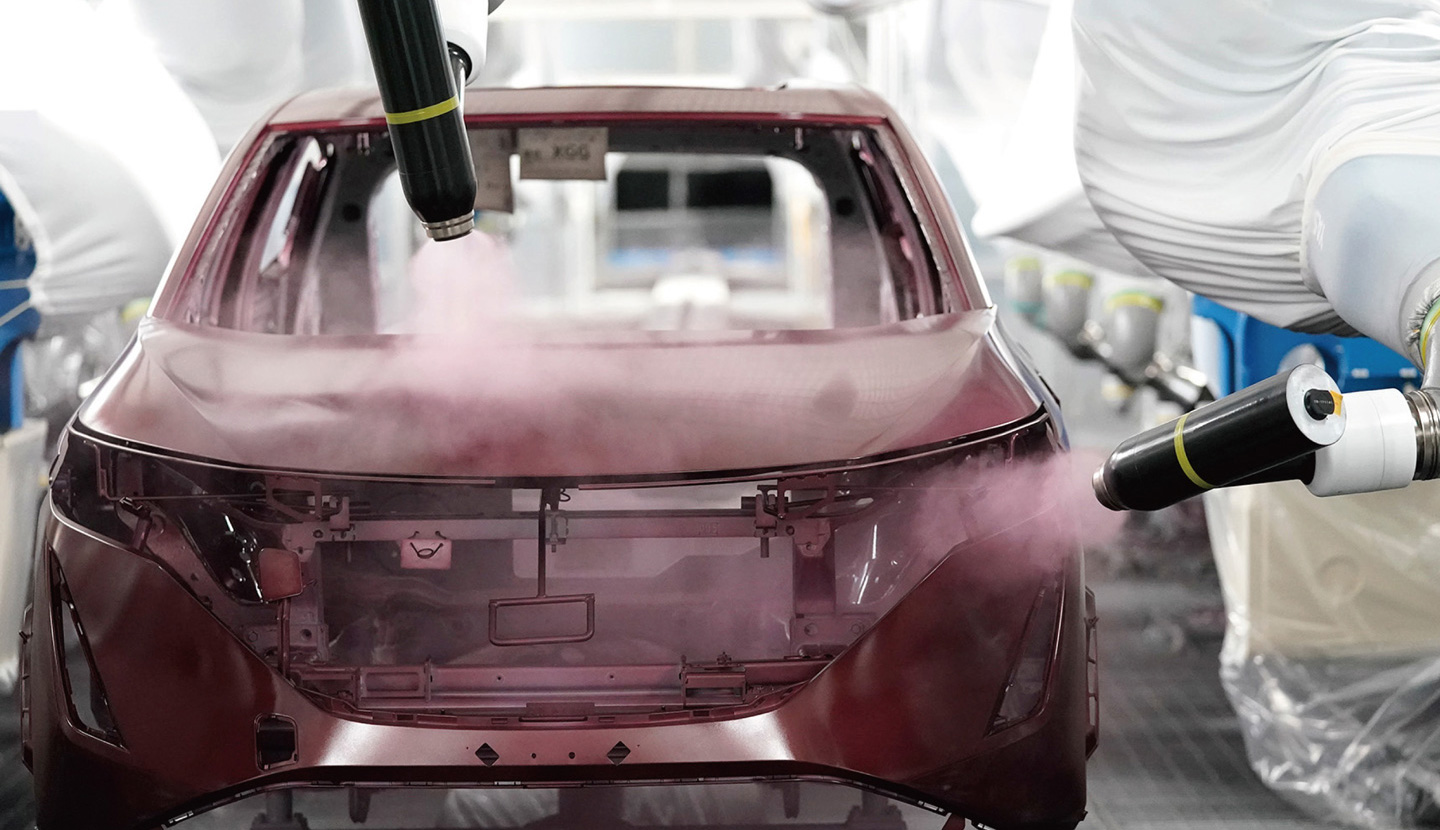

Nissan Intelligent Factory Innovative Paint Lines
Additionally, Nissan has plans for a major expansion to renewable energy generation equipment at its UK Sunderland Plant, which is the largest automotive plant in England. In addition to existing wind turbines and a solar farm, 37,000 solar panels will be added for a 20MW extension. With this expansion, 20% of the plant's energy will be provided by renewable energy produced onsite, and it is expected that renewable energy will be able to supply power for the assembly of Nissan LEAF vehicles sold in Europe.

Renewable energy generator facility at the U.K. Sunderland Plant
Closed-Loop Recycling of Aluminum Parts
Nissan is promoting efforts to reduce CO2 emissions through reducing resource dependency. For example, Nissan has introduced a “closed-loop” recycling system for the all-new 2021 Nissan Rogue at Nissan North America and Nissan Motor Kyushu, and for the all-new Qashqai at Nissan Motor UK, collaborating with aluminum suppliers.
The system helps reduce CO2 emissions compared with using parts made with primary alloys from raw materials. It also promotes the use of materials that don’t rely on newly mined resources, as well as the reduction of waste from factories.
The hood and doors of the 2021 Rogue and the all-new Qashqai are stamped from aluminum alloy, a material that reduces vehicle weight and helps improve fuel efficiency and power performance. Nissan is considering expanding the application of this process to future models and other factories. We will continue to promote efficient and sustainable use of resources, including the use of renewable resources and recyclable materials.
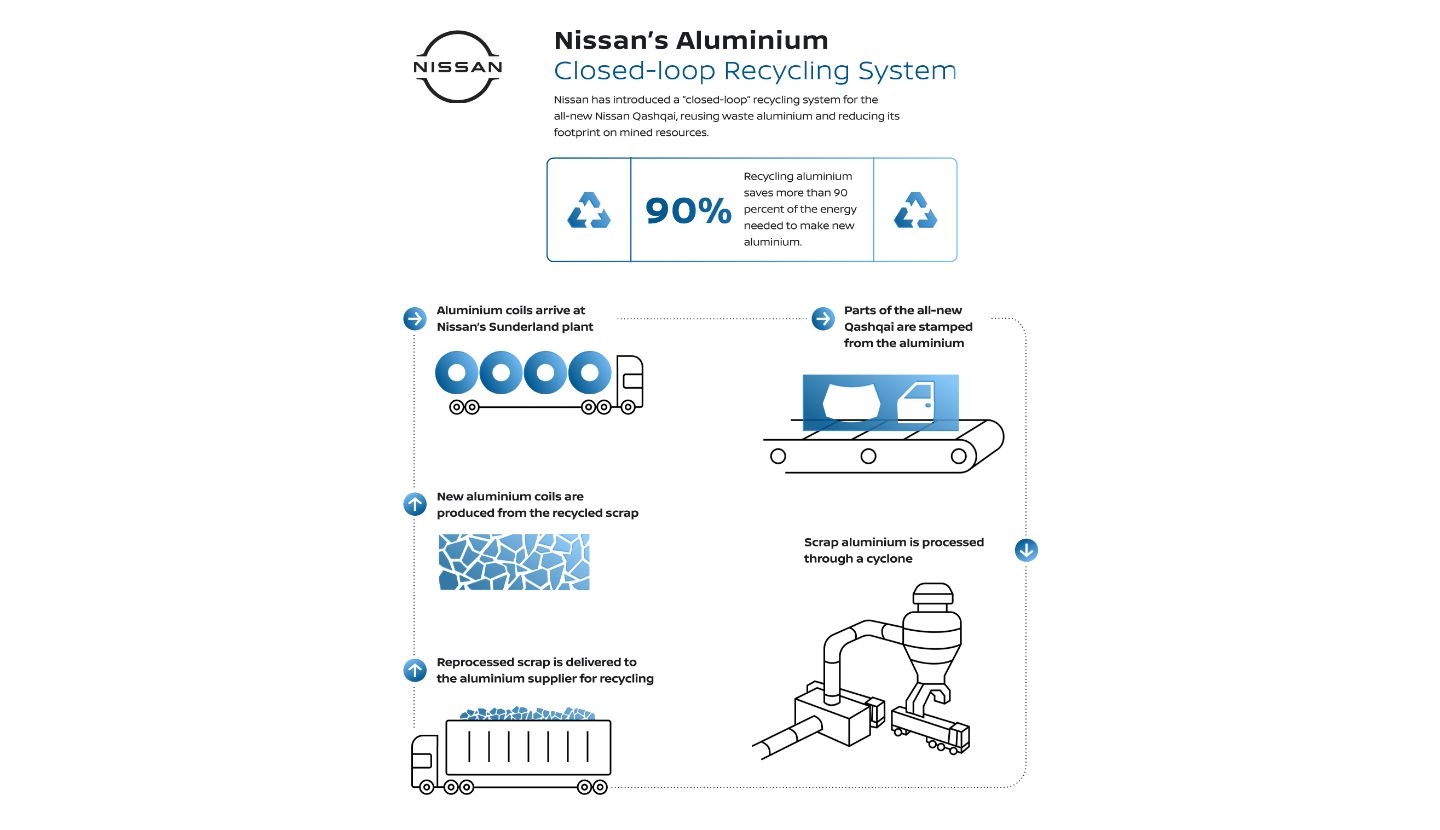
Nissan's Aluminum Closed-loop Recycling System
Road Map to the Future
EV36Zero, the World’s First Electric Vehicle (EV) Hub
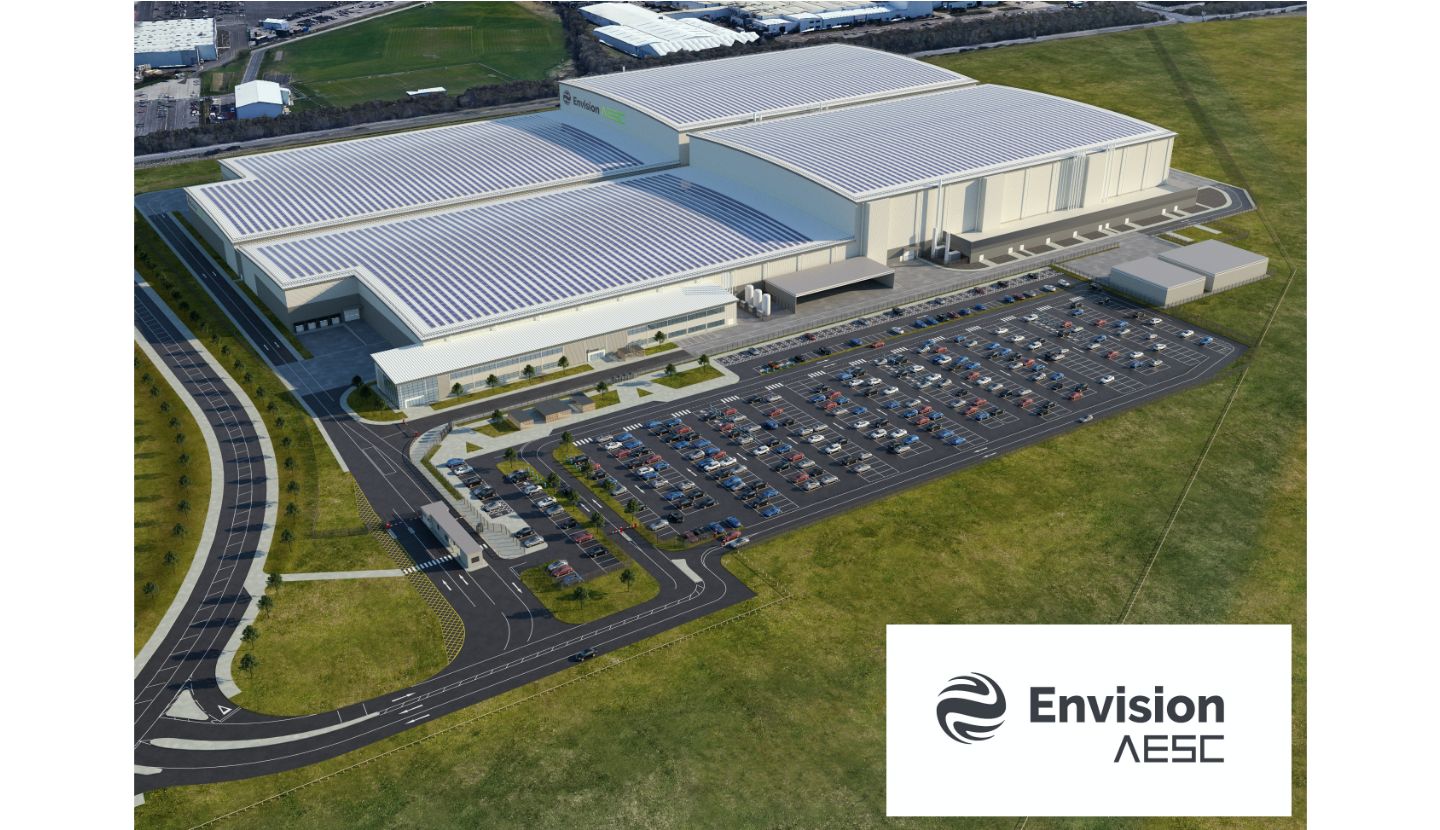
Nissan is a pioneer in achieving carbon neutrality throughout the entire lifecycle of our products. Our comprehensive approach includes not only the development and production of EVs, but also the use of on-board batteries as energy storage and their reuse for secondary purposes. To realize carbon neutrality in Europe with our partners, Nissan unveiled the Nissan EV36Zero, an Electric Vehicle (EV) Hub creating a world-first EV manufacturing ecosystem in July 2021.
- New-generation Nissan electric crossover announced for UK production
- Envision AESC will build a new giga-factory with an annual production capacity of 9GWh adjacent to the Nissan Sunderland Plant
- Renewable energy ‘Microgrid’ to deliver 100% clean electricity for Nissan and its suppliers on the IAMP
- 2nd life EV batteries used as energy storage for ultimate sustainability
- This comprehensive projects represent 6,200 jobs at Nissan and in its UK suppliers
Centered around the plant in Sunderland, UK, Nissan EV36Zero will supercharge the company’s drive to carbon neutrality and establish a new 360-degree solution for zero-emission motoring.
The transformational project has been launched with an initial £1billion investment by Nissan and its partners Envision AESC and Sunderland City Council. Comprised of three interconnected initiatives, Nissan EV36Zero brings together electric vehicles, renewable energy and battery production, setting a blueprint for the future of the automotive industry.
The experience and know-how gained through the project will be shared globally, enhancing Nissan’s global competitiveness. Nissan will continue to leverage its strengths in electrification to become a company that continues to provide value to its customers and society.


