Fifteen years after its debut, the Nissan LEAF continues to shine with life, demonstrating that even as some batteries near the end of their road life, they still have plenty of energy left to offer.
When a Nissan LEAF battery retires from powering a car, it doesn't just fade away. Instead, it embarks on an exciting "second life". Beyond the confines of vehicles, these batteries find innovative uses - harnessing solar energy for schools and supporting off-grid rural communities. Around the world, retired Nissan LEAF batteries are quietly proving their worth by changing lives and pushing the boundaries of what's possible when we rethink and repurpose electric vehicle batteries. Guided by Nissan's 4R Concept – Reuse, Refabricate, Resell, and Recycle – these batteries are integral to building a more sustainable and circular economy, extending their impact far beyond its initial purpose.
Empowering Education – Keeping classrooms bright in South Africa
At Filadelfia School in South Africa, frequent power outages used to disrupt lessons, daily operations, and dorm life. For a boarding school serving 470 students with disabilities, reliable energy is crucial.
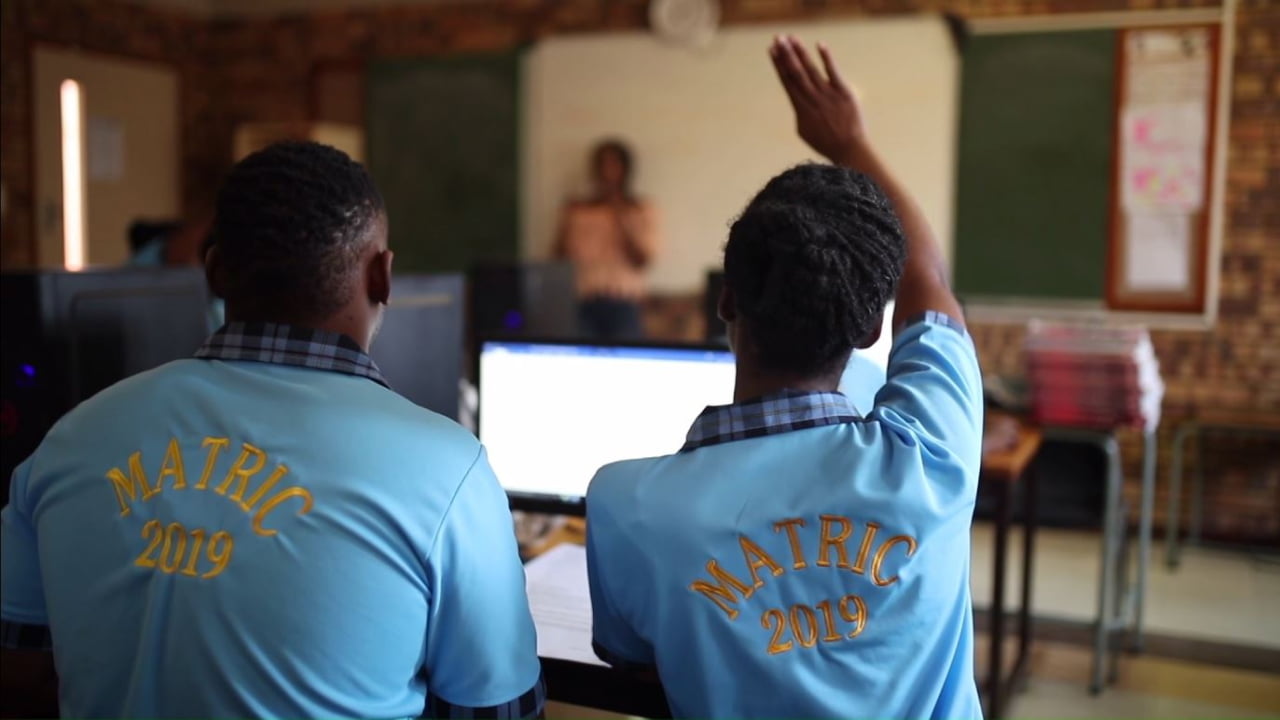

In a classroom at Filadelfia School
"Our deaf students need well-lit classrooms for sign language, and our blind students rely on Braille printers," says Principal Themba Themba. "When the power goes out, everything stops—cooking, learning, even evening study sessions."
That changed with the installation of solar panels paired with repurposed Nissan LEAF batteries. These provide backup power during outages, ensuring classes and dormitories stay functional.
"It's brought stability to the school," says Themba. "Now students can focus on learning without the anxiety of constant interruptions."
Ensuring Energy Resilience – Backing up a city's sole source of power
In Melilla, a Spanish city on the North African coast, reused LEAF batteries help provide stability and power to over 90,000 residents. Isolated from any national grid, the city and its residents entirely depend on a single thermal power plant operated by a subsidiary of multinational energy company Enel. If this plant were to go offline, the entire city would be left without electricity.
To strengthen the city's energy resilience, Nissan partnered with Enel and measurement and control system specialist Loccioni on the "Second Life" project that utilizes used LEAF batteries. In the event of an outage, this storage facility can supply energy to the grid for 15 minutes, which is more than enough time to reset and restart operations. The backup power storage can also store 4 MW of power, easing the load on the main plant while providing up to 1.7 MWh on its own.
Soufiane El Khomri, Director of Energy Services for the Nissan AMIEO (Africa, Middle-East, India, Europe and Oceania) region, explains: "At Nissan, we believe the future is electrified. Our collaboration with Enel allowed us to create a model for a battery's second life, which supports energy resilience and opens up endless possibilities of reusing electric vehicle batteries as part of a circular economy."
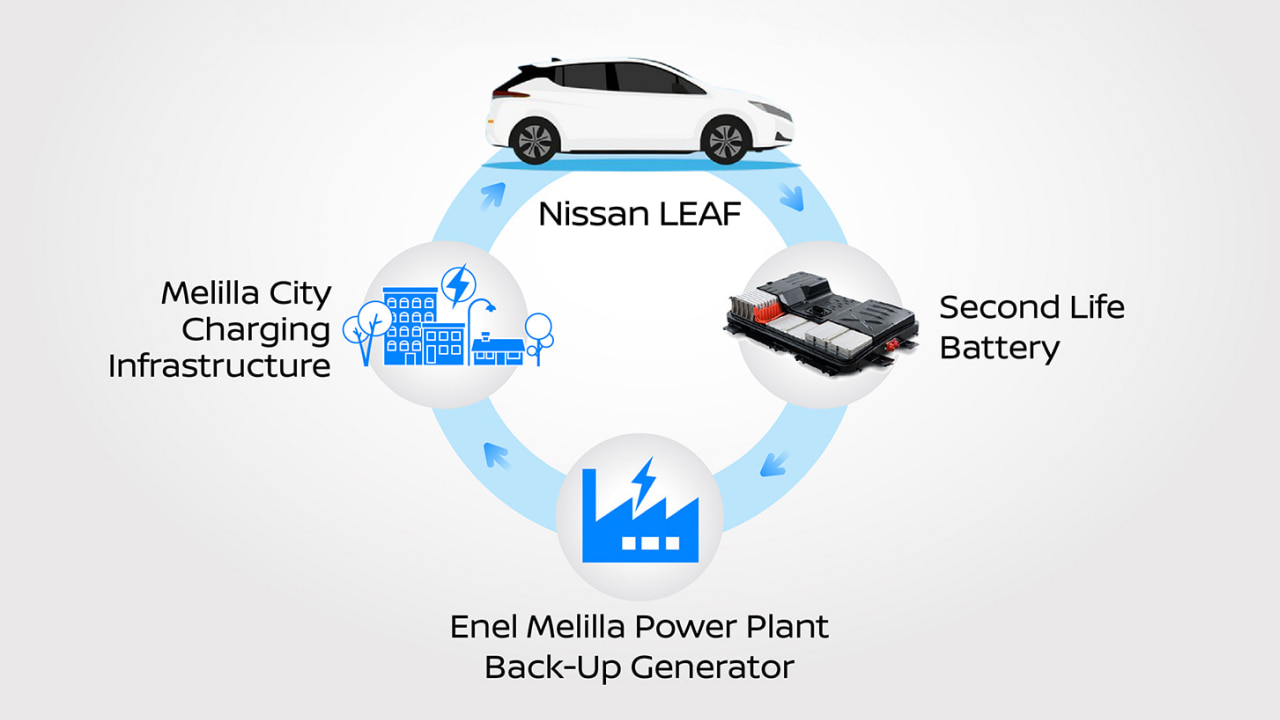
Circular economy model for used car battery
Powering Innovation – Driving factory robots in Japan
If you look inside the factory floor at Nissan's Oppama plant in Japan, you'll find over 700 small robots called AGVs (automated guided vehicles) whizzing along a magnetic track to deliver car parts with precision and speed.
"These batteries have travelled thousands of miles," says Masashi Matsumoto, General Manager of our Production Engineering Research and Development Center, who develops AGVs at Nissan. "Now they're helping us build the next generation of cars while reducing waste."
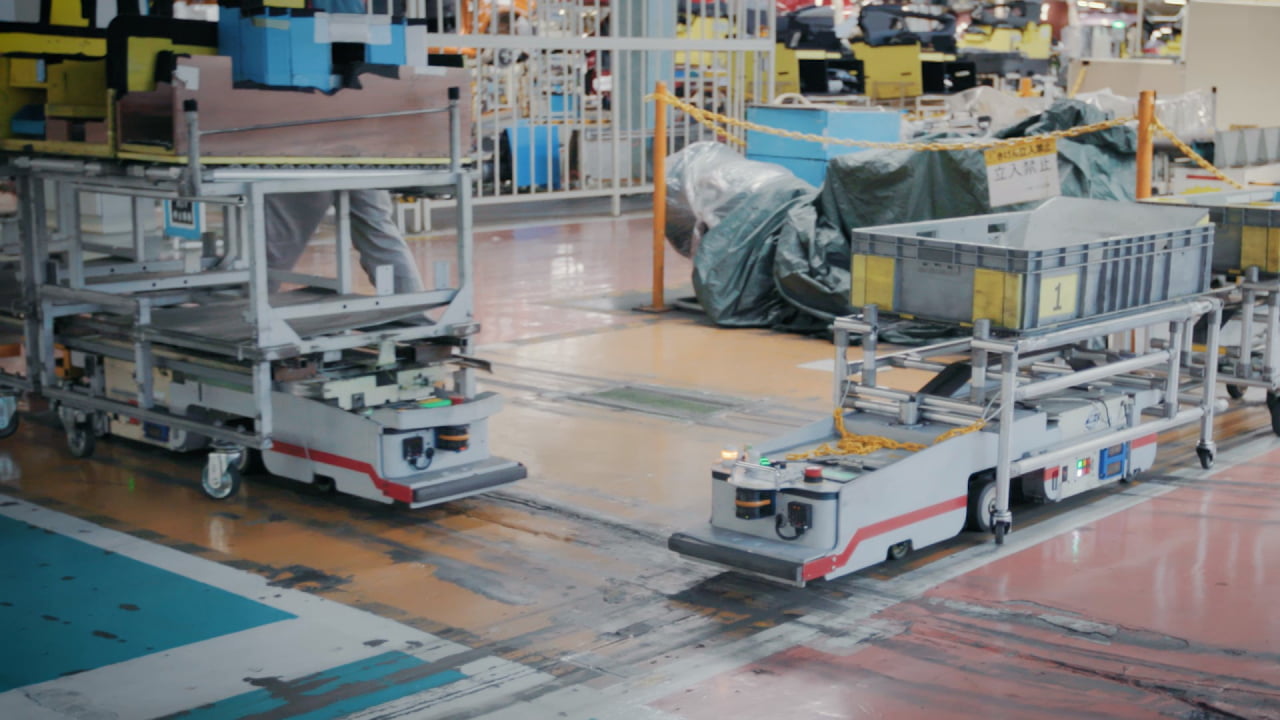

AGVs that run at a Nissan plant
Repurposed batteries in AGVs are expected to last up to eight years—far longer than traditionally used lead-acid batteries—and charge faster, allowing AGVs to briefly top up at charging stations along their routes. This innovation saves time, reduces waste, and helps us create greener, more efficient factories.
Advancing Sustainability – Saving energy at Nissan headquarters in America
Second-life LEAF batteries are creating a more sustainable future at our U.S. headquarters in Franklin, Tennessee. Through the Battery Energy Storage Solution (BESS) project*, these retired batteries store energy during off-peak hours and supply it during peak demand, reducing carbon emissions and lowering energy costs at the Nissan Americas Headquarters.
"On any given day, we typically see two energy demand peaks, depending on the season," says Chris Goddard, regional energy and environmental manager at Nissan. "This project uses second-life batteries to supply stored power during those times, complementing what the building draws from the grid."

Nissan Americas' headquarters lit up at night
The system includes batteries from about 50-60 LEAF vehicles and is expected to cut CO2 emissions by 3.7 tons annually. "It's more than just technology—it's about rethinking how we use resources to build a more sustainable future," Goddard adds.
Transforming Communities – Bringing light to off-grid and previously unreachable regions
Second-life LEAF batteries are also helping communities when they need it most. Teaming up with 4R Energy Corporation, Nissan has created solar-powered streetlights that capture energy and store it using repurposed EV batteries. Free from extra cables or bulky infrastructure, these lights are ideal for remote locations and regions recovering from natural disasters
Since 2018, Nissan and 4R Energy Corporation have brought hope to communities like Namie City in Japan, devastated by the 2011 tsunami, and more recently, Suzu City, affected by the 2024 Noto Earthquake. Beyond illuminating roads, these lights enhance public safety and comfort, supporting recovery efforts and uplifting community spirt.
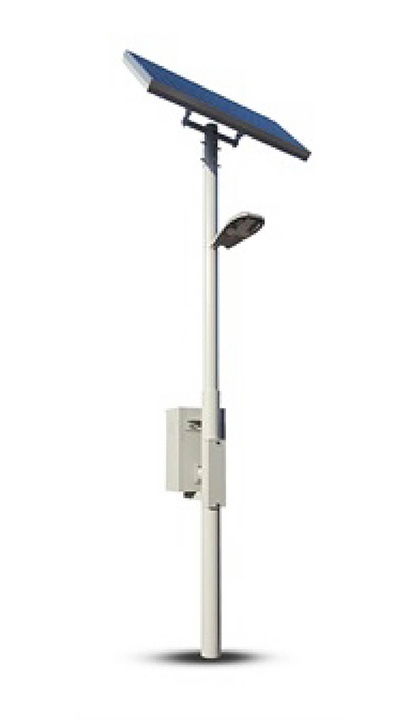

A solar-powered streetlight using repurposed EV batteries
A future with less waste
When a battery powers its final mile on the road, that's not the end of its story. It's the beginning of something bigger. From supporting cities to enhancing daily life, these retired vehicle batteries help us build a more sustainable future.
And it's not just about protecting our planet. As the demand for second-life batteries grows, they add even more value to electric vehicles like the Nissan LEAF, making them an even smarter choice for drivers.
Learn more about our vision for creating a more sustainable future as we move toward carbon neutrality by 2050.
* BESS project collaborates with Middle Tennessee Electric, 7 States Power Corp., and the University of Tennessee-Oak Ridge Innovation Institute.





