Quality Assurance Tools
From
supplier
selection
to
mass-production
processes,
Nissan
has
established
a
unique
system
that
guarantees
reliable
quality.
Quality Assurance system for purchased components from our suppliers
Each component from our suppliers represents the end-product of a complex manufacturing process – including planning and development validation, turning design blueprints into prototypes, performance testing to the final mass production. Nissan has created a system called NPQP*1 for regulating the necessary quality assurance in this entire series of activities. The NPQP requires tests to be carried out on every component from suppliers to ensure the delivery of high quality components from Nissan’s suppliers.
- NPQP stands for Nissan Product Quality Procedure. Nissan created the NPQP based on the standard for automotive sector quality management systems IATF16949, published by the International Automotive Task Force (IATF), to establish supplier quality assurance standards.

Ensuring quality is of utmost importance: Creating an evaluation system for new suppliers
For the NPQP to succeed, we first need to determine each supplier’s ability to provide and respond to feedback. For example, just as you need a driving license to drive a car, we need to check our suppliers’ production sites through a licensing system to ensure that we can build a partnership that will work together. To address this issue, Nissan has developed a system called Automotive-parts Supplier Evaluation Standard (ASES)*. With ASES, companies are evaluated on a five-level scale, classified as A, B, C, or D, and only those in the upper ranks are accepted as suppliers. Each supplier’s actual work site is checked for 240 evaluation criteria, such as whether there is a system in place for clearly identifying non-defective or defective products, and what kind of systems are in place to prevent problems. ASES evaluations are conducted by specially trained evaluators who have passed rigorous tests. These activities lay the foundation for the delivery of accurate parts.
- ASES, the Automotive-parts Supplier Evaluation Standard, is used to evaluate if a vendor qualifies to become a suitable supplier. Based on the evaluation of 240 criteria at five stages, we rank potential vendors as either A, B, C or D, and measure them against the top-ranked industry suppliers.
To maintain consistency in quality: Periodic supplier inspections
Alongside NPQP, Nissan employs a system of checks to maintain quality assurance for suppliers. To visualize the delivery and market quality of suppliers with whom we already do business, we use Supplier Score Card. We also use the Supplier Health Check* system to monitor the health of plants at production sites. Combining these two systems ensures that our suppliers adhere to a system that consistently delivers superior components, and drives them to pursue continuous quality improvement.
*Supplier
Health
Check
In
a
constantly
changing
environment,
the
health
of
a
plant
may
deteriorate
and
affect
quality.
Our
Supplier
Health
Check
system
involves
regularly
diagnosing
the
health
status
of
production
sites
to
prevent
deterioration
in
quality.
We
also
implement
new
quality
initiatives
in
response
to
changing
conditions,
including
the
introduction
of
remote
confirmation
from
fiscal
2020.
Monitoring and improving supplier quality with Supplier Score Card
Nissan creates an individual score card for each supplier called Supplier Score Card, which constantly visualizes the quality status of all suppliers and quickly implement improvement cycles. The overall average score of Nissan’s suppliers is improving year after year. Suppliers with the highest-ranking Supplier Score Card are presented with the Nissan Supplier Quality Award.

Supplier Score Card
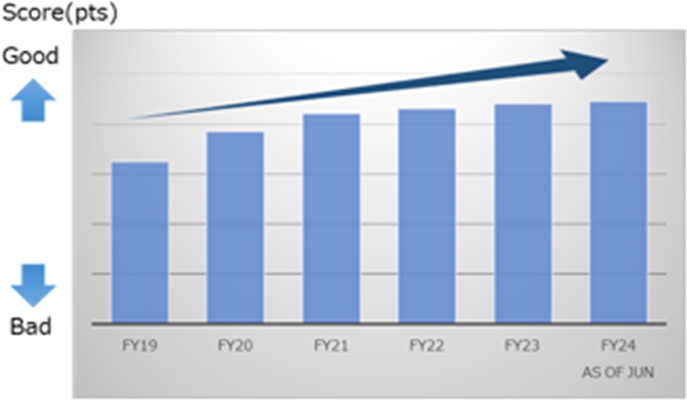
Overall average supplier score

Trophies awarded to suppliers























